For any business, financial forecasting is like looking into a crystal ball. It’s a method of using past financial data and current trends to make projections about how a company will do in the future. In this article, we’ll discuss the meaning and components of financial planning and forecasting, understand how it works using an example, its benefits, and how you can gaze into this crystal ball yourself. Take a peek!
What is Financial Forecasting?
So what is financial forecasting exactly? No one knows the future, so how do you make predictions? The answer is that you use past financial data, analyse income and position statements, and consider current and historical trends to make educated guesses. These guesses help you make well-informed decisions, such as preparing budgets and figuring out how to use your company’s resources wisely for the best outcomes.
How Does Financial Forecasting Work?
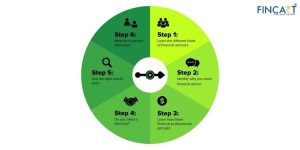
Financial advice is crucial for effective financial forecasting. It provides a clear picture of a company’s future, enabling management to create practical plans to achieve their business goals.
- Analyse the data: A thorough examination of historical data is done. This includes scrutinising past income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. This historical context provides a baseline for understanding how the company has performed in the past.
- Identify the trends: Analysts then identify trends and patterns within this historical data. These trends can be increases or decreases in revenue, changes in profit margins, or shifts in expenses over time.
- Consider the internal factors: This involves understanding the company’s current financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity. The efficiency of internal operations and how well the company manages its resources are looked at. Usually, companies use income statements for internal planning.
- Build models: Financial analysts then construct models and scenarios using the data they’ve collected. These models can be simple spreadsheets or even sophisticated computer simulations. They use mathematical and statistical techniques to project future financial outcomes based on historical trends and the influence of external and internal factors. The scenarios provide a range of possible outcomes, helping companies prepare for various possibilities.
These models provide insights that allow companies to see what their financial picture might look like in the short term or long-term.
Read More: What Are the Main Objectives of Financial Planning?
Components of Financial Forecasting
To help us grasp the concept, let’s explore the components of financial forecasting:
- Projected profit and loss statement: The profit and loss statement, often called the income statement, is a vital part of financial forecasting. It shows how a business makes a profit or suffers a loss during a specific time, usually over a financial year. Predicting the P&L statement helps anticipate future expenses and income, and is an important element in budgeting.
In this statement, you can forecast various items, such as revenue, costs of goods sold, day-to-day operating expenses, depreciation, amortisation, interest income, and interest expenses.
- Balance sheet: It shows a company’s assets like cash reserves, investments, shares, stocks, and equity from investors. It also includes liabilities such as unpaid bills, loan fees, and credit card balances, representing what the company owes.
By using inputs like profit, investments, financial plans, and budgets for cash and capital expenses, one can create a balance sheet forecast. Then a balance sheet can forecast many things such as debt, earnings, liabilities etc.
- Cash flow: While the income statement can predict losses, it doesn’t tell us about available cash. The cash flow statement shows how much money is coming in, going out, and what’s left at the end of the month. Forecasting cash helps management plan for expenses like wages, debt payments, and taxes.
In a Cash Flow statement, you can forecast items like cash from operations, financing activities, investing activities, and the total cash on hand, which helps us figure out how a company can keep operating and adjust its strategies.
- Working Capital: Using the projected balance sheet, income statement, and initial balance sheet we can determine additional funds needed. These funds are referred to as working capital and are used throughout the planning period. With a working capital schedule, you can forecast items like receivable, and payable accounts, prepaid expenses, and other current liabilities.
Types of Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting comes in various forms, both quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative means something that can be measured in quantities or numbers, whereas qualitative is non-numerical and is rather measured by character or quality. All quantitative types of forecasts depend on a lot of historical data that can be measured, statistically analysed, and used to spot trends and patterns. Some of them are:
Time series analysis:
It is useful for recognising trends over some time, particularly in the short term. They can be highly precise.
Straight-line method:
It assumes that a company’s growth rate remains steady, allowing us to predict future values by applying this growth rate to current financials. We calculate the growth rate using the company’s historical data and then multiply it by the current value to obtain the result.
Scenario method:
The scenario method involves analysts creating multiple possible future scenarios and building models to predict how to navigate each unique situation, ultimately aiming for profitability. This approach helps in understanding cause-and-effect relationships among important variables.
Moving average:
They also take historical data and use it to create forecasts for the future. Their primary use is to help identify the direction of a trend. For instance, by looking at sales data from the previous quarter, we can make predictions about sales for the current quarter.
Two common types of moving averages are Simple Moving Averages (SMA) and Exponential Moving Averages (EMA). To calculate a moving average, you add up the values for a given period and then divide by the number of periods.
Pro-forma statements:
These financial statements rely on historical data, such as anticipated variable and fixed costs, as well as sales figures from past years, to create future predictions.
Multiple linear regression:
This method is used when we have multiple variables at play. In such cases, there are numerous independent variables, but just one dependent variable. This technique helps us understand the causes and make reasonably accurate predictions about the dependent variable. Businesses are influenced by multiple factors, so this method is particularly valuable as it considers various variables, making it a dynamic and insightful tool.
Qualitative forecasting methods come into play when there’s limited or no historical data to work with. Some examples of qualitative forecasting methods include:
- Key Assumption Testing: Engaging in key assumption testing involves gathering a set of critical business assumptions and discussing them with key business partners. The main goal is to thoroughly evaluate and validate the potential outcomes associated with these assumptions.
- Business Expertise: Experienced individuals play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of a business. In the absence of data, they can draw upon their deep knowledge, experience, and insights.
- Consumer Research: We conduct consumer research to collect data, both qualitative and quantitative, from potential customers. This data can be gathered through many ways, such as email surveys, phone surveys, questionnaires, sample testing, text-based surveys, in-depth interviews, etc.
Read More: What is Financial Planning Process and How to Execute It?
How to do Financial Forecasting?
Now let’s have a look at some financial forecasting techniques. Here are the key aspects that you need to follow:
- Define the purpose: You need to have a clear purpose. Why are you undertaking this mammoth task? It will provide you with direction and context for the entire forecasting effort. To achieve specific objectives, analysts have to consider different aspects of the business that’s why defining precise goals is essential.
- Gather the data: After clearly defining the purpose, you can start collecting relevant data for the forecast. This includes historical sales and marketing data, along with financial statements. Make sure to have all the data you require, otherwise the forecast will be inaccurate.
- Choose the type of financial forecast: This can be quantitative or qualitative. Every process is different and will provide very specific results so selecting a forecasting method that aligns with the company’s structure and the intended purpose of the forecast is crucial.
- Track your progress: Keeping a record of progress lets managers check results regularly, either in real-time or at planned intervals. This continuous evaluation frees them from time constraints and helps them allocate resources more thoughtfully.
- Analyse the data: Finally, analyse the data thoroughly to assess the effectiveness of the company’s strategies. Based on these findings, you can identify what needs improvement, what works, and what doesn’t.
As you can see, the financial forecasting process is quite complex. A mistake in any of the steps would mean that the forecast will be inaccurate and the time, money, and effort spent achieving it would go to waste. Working based on inaccurate projections can harm you. Before you start the process, you can seek counsel from an experienced financial advisor to ensure your projections are reliable.
Financial Forecasting Example
As you can see from the discussion so far, financial forecasting can be a rather complex process. To grasp the concept more clearly, let’s simplify things by exploring a basic forecast through a straightforward example.
A company produces tables. In the year 2021, they sold Rs. 5 lakh worth of their product. In 2022, they sold tables worth Rs. 5.5 lakh. Can we use this data to project the sales in 2023?
Sure we can!
The company saw a growth of Rs 50k from the year 2021 to 2022. We can use this to calculate the growth rate.
Growth rate = (net growth/sales of 2021)*100
= (50000/500000)*100
= 10%
If we assume that the growth rate will remain constant, we can project the sales of 2023.
10% of sales in 2022 = (10/100)*550000
= Rs. 55,000
So sales for 2023 = Sales of 2022+55000= Rs. 6,05,000
This is a very simple example of the percent of sales method. Remember, this is a very simple example, actual financial forecasts are very intricate and involve a lot more components, processes, and analysis.
Benefits of Financial Forecasting
Here are some ways in which financial forecasting can help a business:
- By anticipating financial challenges and opportunities, financial forecasting helps reduce overall financial risk, contributing to the stability and sustainability of the business.
- It serves as the foundation for creating budgets. By projecting future revenues and expenses, organisations can allocate resources efficiently to meet their strategic goals.
- It equips businesses to prepare for various scenarios, including unexpected expenses. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and ensures stability.
- Financial forecasting provides a structured approach to goal-setting, enabling businesses to set targets that are both attainable and realistic. This ensures that objectives are grounded in the financial realities of the company.
- Businesses can better adapt to fluctuations in demand and shifts in operating costs by using financial forecasts as a guide. This helps them remain competitive.
- By identifying potential financial challenges in advance, financial forecasting helps prevent unforeseen events from derailing business performance, thus enhancing resilience.
Conclusion
Of course, it is impossible to predict the future, but for a business’ longevity, it is essential to not walk into it blindly. With the guidance provided by financial forecasting, a business can get the foresight it needs to navigate the path ahead by making informed decisions and preparing for various scenarios. This intricate process can be made easier with assistance from a skilled investment planner who can make a clear roadmap, designed specifically for a business’s unique goals.